 this dude is guilty as fuck.... this shit is ridiculous....
this dude is guilty as fuck.... this shit is ridiculous....
Intimidation, Pressure and Humiliation: Inside Trump’s Two-Year War on the Investigations Encircling Him
https://www.nytimes.com/2019/02/19/us/politics/trump-investigations.html
WASHINGTON — As federal prosecutors in Manhattan gathered evidence late last year about President Trump’s role in silencing women with hush payments during the 2016 campaign, Mr. Trump called Matthew G. Whitaker, his newly installed attorney general, with a question. He asked whether Geoffrey S. Berman, the United States attorney for the Southern District of New York and a Trump ally, could be put in charge of the widening investigation, according to several American officials with direct knowledge of the call.
Mr. Whitaker, who had privately told associates that part of his role at the Justice Department was to “jump on a grenade” for the president, knew he could not put Mr. Berman in charge, since Mr. Berman had already recused himself from the investigation. The president soon soured on Mr. Whitaker, as he often does with his aides, and complained about his inability to pull levers at the Justice Department that could make the president’s many legal problems go away.
Trying to install a perceived loyalist atop a widening inquiry is a familiar tactic for Mr. Trump, who has been struggling to beat back the investigations that have consumed his presidency. His efforts have exposed him to accusations of obstruction of justice as Robert S. Mueller III, the special counsel, finishes his work investigating Russian interference in the 2016 election.
Mr. Trump’s public war on the inquiry has gone on long enough that it is no longer shocking. Mr. Trump rages almost daily to his 58 million Twitter followers that Mr. Mueller is on a “witch hunt” and has adopted the language of Mafia bosses by calling those who cooperate with the special counsel “rats.” His lawyer talks openly about a strategy to smear and discredit the special counsel investigation. The president’s allies in Congress and the conservative media warn of an insidious plot inside the Justice Department and the F.B.I. to subvert a democratically elected president.
Subscribe to The Times
Mr. Whitaker, who earlier this month told a congressional committee that Mr. Trump had never pressured him over the various investigations, is now under scrutiny by House Democrats for possible perjury.
A Justice Department spokeswoman said that the White House had not asked Mr. Whitaker to interfere in the investigations. “Under oath to the House Judiciary Committee, then Acting Attorney General Whitaker stated that ‘at no time has the White House asked for nor have I provided any promises or commitments concerning the special counsel’s investigation or any other investigation,’” said the spokeswoman, Kerri Kupec. “Mr. Whitaker stands by his testimony.”
The White House declined to comment for this article.
The story of Mr. Trump’s attempts to defang the investigations has been voluminously covered in the news media, to such a degree that many Americans have lost track of how unusual his behavior is. But fusing the strands reveals an extraordinary story of a president who has attacked the law enforcement apparatus of his own government like no other president in history, and who has turned the effort into an obsession. Mr. Trump has done it with the same tactics he once used in his business empire: demanding fierce loyalty from employees, applying pressure tactics to keep people in line, and protecting the brand — himself — at all costs.
hounded by his “deep state” foes. The new Democratic majority in the House, and the prospect of a wave of investigations on Capitol Hill this year, will test whether the strategy shores up Mr. Trump’s political support or puts his presidency in greater peril. The president has spent much of his time venting publicly about there being “no collusion” with Russia before the 2016 election, which has diverted attention from a growing body of evidence that he has tried to impede the various investigations.
Julie O’Sullivan, a criminal law professor at Georgetown University, said she believed there was ample public evidence that Mr. Trump had the “corrupt intent” to try to derail the Mueller investigation, the legal standard for an obstruction of justice case.
But this is far from a routine criminal investigation, she said, and Mr. Mueller will have to make judgments about the impact on the country of making a criminal case against the president. Democrats in the House have said they will wait for Mr. Mueller to finish his work before making a decision about whether the president’s behavior warrants impeachment.
In addition to the Mueller investigation, there are at least two other federal inquiries that touch the president and his advisers — the Manhattan investigation focused on the hush money payments made by Mr. Trump’s lawyer, Michael D. Cohen, and an inquiry examining the flow of foreign money to the Trump inaugural committee.
The president’s defenders counter that most of Mr. Trump’s actions under scrutiny fall under his authority as the head of the executive branch. They argue that the Constitution gives the president sweeping powers to hire and fire, to start and stop law enforcement proceedings, and to grant presidential pardons to friends and allies. A sitting American president cannot be indicted, according to current Justice Department policy.
Mr. Trump’s lawyers add this novel response: the president has been public about his disdain for the Mueller investigation and other federal inquiries, so he is hardly engaged in a conspiracy. He fired one F.B.I. director and considered firing his replacement. He humiliated his first attorney general for being unable to “control” the Russia investigation and installed a replacement, Mr. Whitaker, who has told people he believed his job was to protect the president. But that, they say, is Donald Trump being Donald Trump.
In other words, the president’s brazen public behavior might be his best defense.
The first crisis
resignation of Michael T. Flynn, the national security adviser, the previous night. Mr. Flynn, who had been a top campaign adviser to Mr. Trump, was under investigation by the F.B.I. for his contacts with Russians and secret foreign lobbying efforts for Turkey.
The Justice Department had already raised questions that Mr. Flynn might be subject to blackmail by the Russians for misleading White House officials about the Russian contacts, and inside the White House there was a palpable fear that the Russia investigation could consume the early months of a new administration.
As the group in the Oval Office talked, one of Mr. Trump’s advisers mentioned in passing what then-Speaker Paul D. Ryan of Wisconsin had told reporters — that Mr. Trump had asked Mr. Flynn to resign.
It was unclear where Mr. Ryan had gotten that information, but Mr. Trump seized on Mr. Ryan’s words. “That sounds better,” the president said, according to people with knowledge of the discussions. Mr. Trump turned to the White House press secretary at the time, Sean Spicer, who was preparing to brief the media.
“Say that,” Mr. Trump ordered.
But was that true, Mr. Spicer pressed.
“Say that I asked for his resignation,” Mr. Trump repeated.
The president appeared to have little concern about what he told the public about Mr. Flynn’s departure, and quickly warmed to the new narrative. The episode was among the first of multiple ham-handed efforts by the president to carry out a dual strategy: publicly casting the Russia story as an overblown hoax and privately trying to contain the investigation’s reach.
a new book by Chris Christie, a former New Jersey governor and a longtime Trump ally.
Mr. Trump finally fired Mr. Comey in May. But the president and the White House gave conflicting accounts of their reasoning for the dismissal, which only served to exacerbate the president’s legal exposure.
A week after the firing, The New York Times disclosed that the president had asked Mr. Comey to end the Flynn investigation. The next day, the deputy attorney general, Rod J. Rosenstein, appointed Mr. Mueller, a Republican, as special counsel.
Instead of ending the Russia investigation by firing Mr. Comey, Mr. Trump had drastically raised the stakes.
Boiling frustration
Mr. Mueller’s appointment fueled Mr. Trump’s anger and what became increasingly reckless behavior — triggering a string of actions over the summer of 2017 that could end up as building blocks in a case by Congress that the president engaged in a broad effort to thwart the investigation.
On Twitter and in news media interviews, Mr. Trump tried to pressure investigators and undermine the credibility of potential witnesses in the Mueller investigation.
He directed much of his venom at Mr. Sessions, who had recused himself in March from overseeing the Russia investigation because of contacts he had during the election with Russia’s ambassador to the United States.
said during an interview with The Times that he never would have named Mr. Sessions attorney general if he had known Mr. Sessions would step aside from the investigation.
Privately, he tried to remove Mr. Sessions — he said he wanted an attorney general who would protect him — but didn’t fire him, in part because White House aides dodged the president’s orders to demand his resignation. Mr. Trump even called his former campaign manager, Corey Lewandowski, over the Fourth of July weekend to ask him to pressure Mr. Sessions to resign. Mr. Lewandowski was noncommittal and never acted on the request.
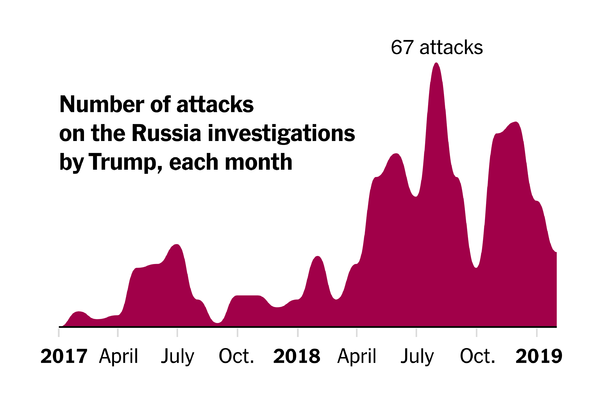
Trump Has Publicly Attacked the Russia Investigation More Than 1,100 Times
President Trump has publicly criticized federal investigations, opening him up to possible obstruction of justice charges.
Feb. 19, 2019
One of Mr. Trump’s lawyers also reached out that summer to the attorneys for two of his former aides — Paul J. Manafort and Mr. Flynn — to discuss possible pardons. The discussions raised questions about whether the president was willing to offer pardons to influence their decisions about whether to plead guilty and cooperate in the Mueller investigation.
The president even tried to fire Mr. Mueller himself, a move that could have brought an end to the investigation. Just weeks after Mr. Mueller’s appointment, the president insisted that he ought to be fired because of perceived conflicts of interest. Mr. Trump’s White House counsel, Donald F. McGahn II, who would have been responsible for carrying out the order, refused and threatened to quit.
The president eventually backed off.
A new strategy: discrediting an investigation
the first call for the appointment of a second special counsel to essentially reinvestigate Hillary Clinton for her handling of her emails while secretary of state — the case had ended in the summer of 2016 — as well as the origins of the F.B.I.’s investigation of Mr. Flynn and other Trump associates.
The letter itself, with the signatures of only 20 House Republicans, gained little traction at first. But an important shift was underway: At a time when Mr. Trump’s lawyers were urging him to cooperate with Mr. Mueller and tone down his Twitter feed, the president’s fiercest allies in Congress and the conservative media were busy trying to flip the script on the federal law enforcement agencies and officials who began the inquiry into Mr. Trump’s campaign.
Mr. Gaetz and Mr. Jordan began huddling with like-minded Republicans, sometimes including Representative Mark Meadows, a press-savvy North Carolinian close to Mr. Trump, and Representative Devin Nunes of California, the head of the House Intelligence Committee.
Mr. Nunes, the product of a dairy farming family in California’s Central Valley, had already emerged as one of Mr. Trump’s strongest allies in Congress. He worked closely with Mr. Flynn during the Trump transition after the 2016 election, and he had a history of battling the C.I.A. and other intelligence agencies, which he sometimes accused of coloring their analysis for partisan reasons. In the spring of 2017, he sought to bolster Mr. Trump’s false claim that President Barack Obama had ordered an illegal wiretap on Trump Tower.
Using Congress’s oversight powers, the Republican lawmakers succeeding in doing what Mr. Trump could not realistically do on his own: forcing into the open some of the government’s most sensitive investigative files — including secret wiretaps and the existence of an F.B.I. informant — which were part of the Russia inquiry. House Republicans opened investigations into the F.B.I.’s handling of the Clinton email case and a debunked Obama-era uranium deal indirectly linked to Mrs. Clinton. The lawmakers got a big assist from the Justice Department, which gave them private text messages recovered from two senior F.B.I. officials who had been on the Russia case. The officials — Peter Strzok and Lisa Page — repeatedly criticized Mr. Trump in their texts, which were featured in a loop on Fox News and became a centerpiece of an evolving and powerful conservative narrative about a cabal inside the F.B.I. and Justice Department to take down Mr. Trump.
The president cheered the lawmakers on Twitter, in interviews and in private, urging Mr. Gaetz on Air Force One in December 2017 and in subsequent phone calls to keep up the House Republicans’ oversight work. He was hoping for fair treatment from Mr. Mueller, Mr. Trump told Mr. Gaetz in one of the calls just after the congressman appeared on Fox News, but that did not preclude him from encouraging his allies’ scrutiny of the investigation.
a memo alleging that the F.B.I. had abused its authority in spying on a former Trump campaign associate, Carter Page, Mr. Trump called Mr. Nunes a “Great American hero.”(The F.B.I. said it had “grave concerns” about the memo’s accuracy.)
repeatedly leaned on administration officials on behalf of the lawmakers — urging Mr. Rosenstein and other law enforcement leaders to flout procedure and share sensitive materials about the ongoing case with Congress. As president, Mr. Trump has ultimate authority over information that passes through the government, but his interventions were unusual.
By the spring of 2018, Mr. Nunes zeroed in on new targets. In one case, he threatened to hold Mr. Rosenstein in contempt of Congress or even try to impeach him if the documents he wanted were not turned over, including the file used to open the Russia case. In another, he pressed the Justice Department for sensitive information about a trusted F.B.I. informant used in the Russia investigation, a Cambridge professor named Stefan Halper — even as intelligence officials said that the release of the information could damage relationships with important allies.
The president chimed in, accusing the F.B.I., without evidence, of planting a spy in his campaign. “SPYGATE could be one of the biggest political scandals in history!” Mr. Trump wrote, turning the term into a popular hashtag.
Most Senate Republicans tried to ignore the House tactics, and not all House Republicans who participated in the investigations agreed with the scorched-earth approach. Representative Trey Gowdy, a South Carolina Republican and former federal prosecutor who had led Republicans in the Benghazi investigation, felt that figures like Mr. Gaetz and, in some cases, Mr. Nunes, were hurting their own cause with a sloppy, overhyped campaign that damaged Congress’s credibility.
Former Representative Thomas J. Rooney, a Republican who sat on the Intelligence Committee and retired last year, was similarly critical. “The efforts to tag Mueller as a witch hunt are a mistake,” he said in an interview. “The guy is an American hero. He is somebody who has always spouted the rule of law in what our country is about.”
But Mr. Gaetz makes no apologies.
“Do I think it’s right that our work in the Congress has aided in the president’s defense?” he asked, before answering his own question.
of bias and ignoring facts to carry out an anti-Trump agenda. He called one of Mr. Mueller’s top prosecutors, Andrew Weissmann, a “complete scoundrel.”
Behind the scenes, Mr. Giuliani was getting help from a curious source: Kevin Downing, the lawyer for Paul Manafort, who had been the president’s 2016 campaign chairman. Mr. Manafort had agreed to cooperate with the special counsel after being convicted of financial crimes in an attempt to lessen a potentially lengthy prison sentence. Mr. Downing shared details about prosecutors’ lines of questioning, Mr. Giuliani admitted late last year.
It was a highly unusual arrangement — the lawyer for a cooperating witness providing valuable information to the president’s lawyer at a time when his client remained in the sights of the special counsel’s prosecutors. The arrangement angered Mr. Mueller’s investigators, who questioned what Mr. Manafort was trying to gain from the arrangement.
showed a 14-point uptick in the percentage of Americans polled who disapproved of how Mr. Mueller was handling the inquiry. “Mueller is now slightly more distrusted than trusted, and Trump is a little ahead of the game,” Mr. Giuliani said during an interview in August.
“So I think we’ve done really well,” Mr. Giuliani added. “And my client’s happy.”
The F.B.I. raids Michael Cohen
ordered him during the 2016 campaign to buy the silence of women who claimed they had sex with the president. In a separate bid for leniency, Mr. Cohen told Mr. Mueller’s prosecutors about Mr. Trump’s participation in negotiations during the height of the presidential campaign to build a Trump Tower in Moscow.
Mr. Trump was now battling twin investigations that seemed to be moving ever close to him. And Mr. Cohen, once the president’s fiercest defender, was becoming his chief tormentor.
In a court appearance in August, Mr. Cohen pleaded guilty and told a judge that Mr. Trump had ordered him to arrange the payments to the women, Stormy Daniels and Karen McDougal. Mr. Cohen’s descriptions of the president’s actions made Mr. Trump, in effect, an unindicted co-conspirator and raised the prospect of the president being charged after he leaves office. Representative Jerrold Nadler, the New York Democrat who in January became the chairman of the House Judiciary Committee, which has jurisdiction over the matter, said the implied offense was probably impeachable.
infuriated Democratic lawmakers, who claimed the president was trying to threaten and intimidate a witness ahead of testimony Mr. Cohen planned before Congress.
“He’s only been threatened by the truth,” the president responded.
Another attorney general takes office
As the prosecutors closed in, Mr. Trump felt a more urgent need to gain control of the investigation.
He made the call to Mr. Whitaker to see if he could put Mr. Berman in charge of the New York investigation. The inquiry is run by Robert Khuzami, a career prosecutor who took over after Mr. Berman, whom Mr. Trump appointed, recused himself because of a routine conflict of interest.
What exactly Mr. Whitaker did after the call is unclear, but there is no evidence that he took any direct steps to intervene in the Manhattan investigation. He did, however, tell some associates at the Justice Department that the prosecutors in New York required “adult supervision.”
William P. Barr was sworn in as attorney general on Thursday. Many officials at the Justice Department hope he will try to change the Trump administration’s combative tone toward the department as well as the F.B.I.CreditSarah Silbiger/The New York Times

Image

William P. Barr was sworn in as attorney general on Thursday. Many officials at the Justice Department hope he will try to change the Trump administration’s combative tone toward the department as well as the F.B.I.CreditSarah Silbiger/The New York Times
Second, Mr. Trump moved on to a new attorney general, William P. Barr, whom Mr. Trump nominated for the job in part because of a memo Mr. Barr wrote last summer making a case that a sitting American president cannot be charged with obstruction of justice for acts well within his power — like firing an F.B.I. director.
A president cannot be found to have broken the law, Mr. Barr argued, if he was exercising his executive powers to fire subordinates or use his “complete authority to start or stop a law enforcement proceeding.”
The memo might have ingratiated Mr. Barr to his future boss, but Mr. Barr is also respected among the rank and file in the Justice Department. Many officials there hope he will try to change the Trump administration’s combative tone toward the department as well as the F.B.I.
ADVERTISEMENT
Whether it is too late is another question. Mr. Trump's language, and allegations of “deep state” excesses, are now embedded in the political conversation, used as a cudgel by the president’s supporters.
This past December, days before Mr. Flynn was to be sentenced for lying to the F.B.I., his lawyers wrote a memo to the judge suggesting that federal agents had tricked the former national security adviser into lying. The judge roundly rejected that argument, and on sentencing day he excoriated Mr. Flynn for his crimes.
The argument about F.B.I. trickery did, however, appear to please the one man who holds great power over Mr. Flynn’s future — the constitutional power to pardon.
“Good luck today in court to General Michael Flynn,” Mr. Trump tweeted cheerily on the morning of the sentencing.


